Achilles Tendonitis
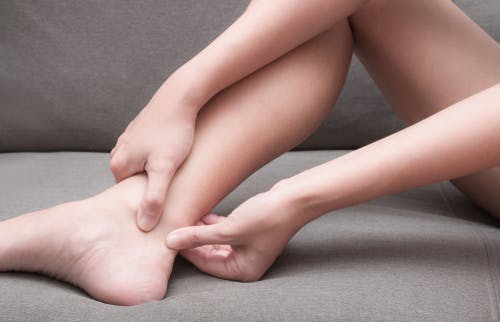
Achilles tendonitis is inflammation of the Achilles tendon and involves pain in the Achilles tendon or at the insertion of the Achilles tendon into the heel bone (calcaneus). In most cases, it is classified as an overuse injury - whereby the tendon is overloaded over a period of time. There may not be one particular activity that has precipitated the condition. People who perform regular sporting activity can suffer from Achilles tendonitis, but it is also a common overuse injury in people that do not participate in sport.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis
- pain in the back of the heel
- difficulty walking – sometimes the pain makes walking impossible
- swelling, tenderness and warmth of the Achilles tendon
- irritation of the Achilles tendon when wearing certain shoes.
Causes of Achilles Tendonitis
- Overuse injury – When the Achilles tendon is stressed it can develop small tears. Often runners can develop Achilles Tendonitis due to the repetitive movement. People who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball, are also at increased risk.
- Arthritis – Achilles tendonitis can be a part of generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis.
- Foot posture – some people with flat feet or collapsed, "low arch" feet can develop Achilles tendonitis. The flattened arch can shorten the Achilles tendon as well as the calf muscle. This constant mechanical stress on the heel and tendon can cause inflammation, pain and swelling of the tendon.
- Footwear – wearing shoes with minimal support while walking or running can increase the risk, as can wearing high heels. Very flat shoes like minimalist running shoes or ballet flats can increase tension on the Achilles Tendon.
- Overweight and obesity – being overweight places more strain on many parts of the body, including the Achilles tendon.
Diagnosis of Achilles Tendonitis
When you present to the Podiatrist, a Biomechanical Assessment will be conducted. In this assessment, we will take a full history which will include your exercise regime and the type of shoes you wear. The physical examination will include palpation of your Achilles Tendon - looking for any thickening or tenderness in the Achilles Tendon. We may need to refer you for X-Ray or Ultrsasound to show us the quality of your bones and tendons. This is generally enough information for us formulate a diagnosis and also direct you to a treatment pathway which will get you back to doing what you want to do as soon as possible.
Achilles Tendonitis Treatment
The aim of the treatment is to reduce strain on the tendon and reduce inflammation. Treatment may include;
- Avoiding or severely limiting activities that may aggravate the condition, such as running
- Orthoses can take pressure off the tendon as it heals. In cases of flat or hyperpronated feet, your Podiatrist may recommend long-term use of orthoses as the problem is likely to recur if the problem is due to poor foot function
- Heel raises to reduce tension on the Achilles Tendon
- Strengthening the calf muscle which will also improve Achilles Tendon strength
- Reduce the use of very flat shoes and high heels
- Dry Needling to improve blood flow to speed up tendon healing time
- Applying icepacks for 20 minutes per hour during the acute stage
- Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- The use of a walking boot or "moon boot" to reduce movement and completely offload the tendon to give it time to heal. This can be recommended in severe cases and used for up to 8 weeks.
WARNING! Recovery from Achilles Tendonitis is often slow and full recovery will depend on the severity of your condition and how well you follow your treatment plan!